“It is no use saying, ‘We are doing our best.’ You have got to succeed in doing what is necessary.” – Winston Churchill
Dear Readers,
Sorry – one day late this week due to the Easter break.
An unmanned stealth torpedo, nuclear powered, that travels underwater until it reaches its target then delivers a “warhead of multiple megatons … causing radioactive waves that would render swathes of the target coastline uninhabitable for decades,” as described by CNN citing Russian officials. It has already begun testing which is scheduled to continue throughout the year.
This is one of a new range of nuclear and advanced weapons announced by Russia’s President Vladimir Putin at the Manezh Central Exhibition Hall near the Kremlin on 1 March, 2018.
Other weapons are reported to include a nuclear powered cruise missile, newly designed components to intercontinental ballistic missiles, a hypersonic boost glide vehicle as well as the new torpedo.
Without doubt Russia and China are designing weapons that are intentionally much faster, with a longer range, and with greater destructive power on arrival. Not only is this strategic threat developing outside of the possibilities of new and better arms controls agreements, both Russia and China are looking to broaden their control over traditional horizons. Russia is building up its presence and capability along its Arctic coastline while China continues its ‘ocean grab’ in the South and East China Seas.
Without mutually respected international checks and balances, this is a situation that could get out of hand very quickly, and very seriously.
Editor
Photo Quiz – Commanders
Another set of pictures for you to ponder- this time great commanders. Again no prizes, but the answers are at the end of this email.
1).
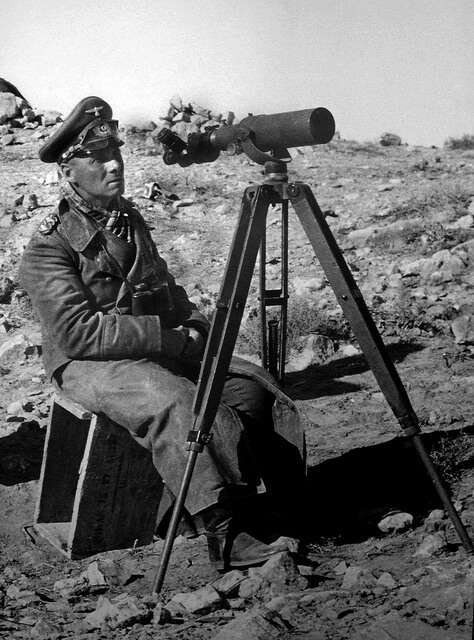 2).
2).
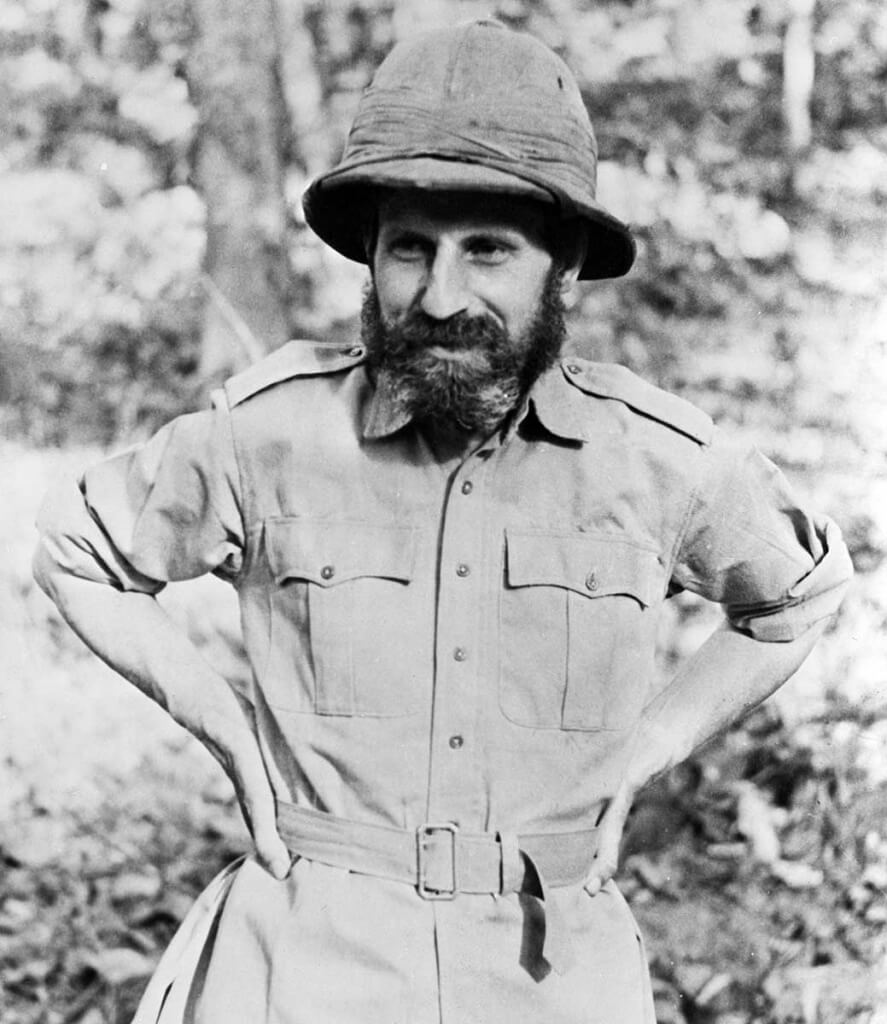 3).
3).
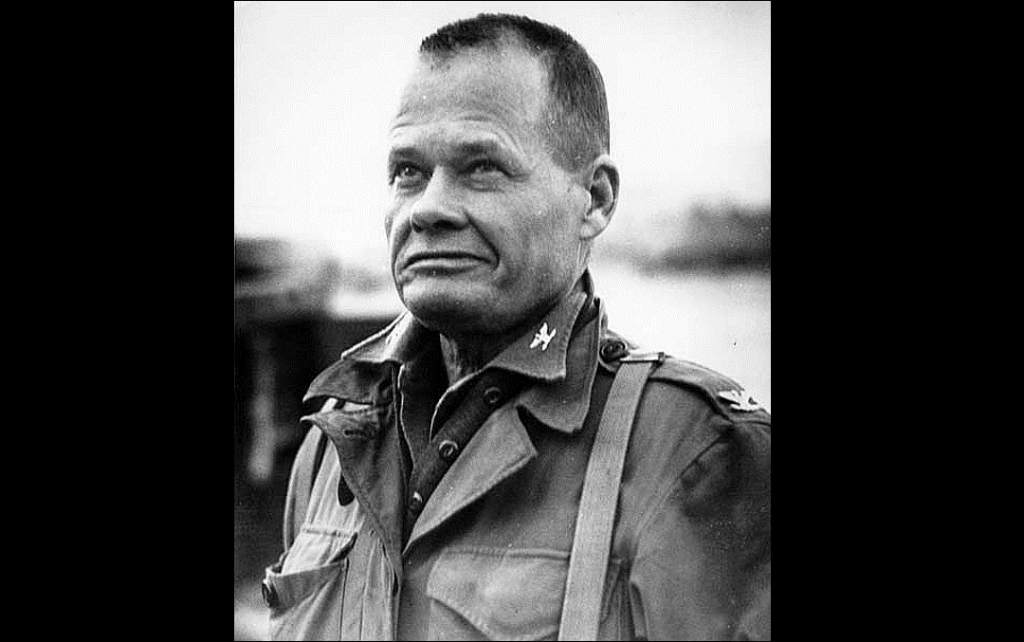

DARPA SEEKS TO MEASURE THE VALUE OF FUTURE QUANTUM COMPUTING
How do you measure the potential value of quantum computing? The US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) has just announced its Quantum Benchmarking programme to do just that. DARPA believes that quantum computers will help to solve particular ‘military-relevant’ problems.
The definition of quantum computing is “the use of quantum phenomena such as superposition and entanglement to perform computation.”
Looking for an explanation that I (your Editor) could understand I came across an explanation online by Amit Katwala on Wired (www.wired.co.uk/article/quantum-computing-explained 5 March 2020).
“Take a coin. If you flip it, it can either be heads or tails. But if you spin it – it’s got a chance of landing on heads, and a chance of landing on tails. Until you measure it, by stopping the coin, it can be either. Superposition is like a spinning coin, and it’s one of the things that makes quantum computers so powerful. A qubit allows for uncertainty.
If you ask a normal computer to figure its way out of a maze, it will try every single branch in turn, ruling them all out individually until it finds the right one. A quantum computer can go down every path of the maze at once. It can hold uncertainty in its head.”
“It’s really about developing quantum computing yardsticks that can accurately measure what’s important to focus on in the race toward large, fault-tolerant quantum computers,” said Joe Altepeter, programme manager in DARPA’s Defense Sciences Office. “Building a useful quantum computer is really hard, and it’s important to make sure we’re using the right metrics to guide our progress towards that goal. If building a useful quantum computer is like building the first rocket to the moon, we want to make sure we’re not quantifying progress toward that goal by measuring how high our planes can fly.”
According to Altepeter, ““Quantum Benchmarking is focused on the fundamental question: How will we know whether building a really big fault-tolerant quantum computer will revolutionise an industry?”
He added: “Companies and government researchers are poised to make large quantum computing investments in the coming decades, but we don’t want to sprint ahead to build something and then try to figure out afterward if it will be useful for anything.”
DARPA has already made investment into quantum research that has resulted in foundational progress in developing next-generation military capabilities such as positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) in GPS-denied environments; quantum computing; and ultra-secure communications.
RUSI TRACKS UK’S INTEGRATED REVIEW
On Wednesday 31 March the Royal United Services Institute (RUSI) held a virtual discussion on Global Britain in a Competitive Age: Taking Stock of the Integrated Review between its deputy director general, Professor Malcolm Chalmers, and Lord Ricketts, the United Kingdom’s first National Security Adviser and permanent under-secretary at the Foreign and Commonwealth Office (FCO), who provided oversight for the National Security Strategy and Strategic Defence Review in 2010.
Following the Government’s release of the Integrated Review, Prof Chalmers authored a RUSI paper entitled The Integrated Review: The UK as a Reluctant Middle Power?
Here are some of the soundbites from the discussion that took place. Prof Chambers began by stating that he believe that the latest review represented “a significant advance on the last two defence security reviews” in that it “broadened the concept of national security to include economic security.”
The review was handicapped by its seemingly lack of political acceptance that the UK was a medium power rather than a superpower said Prof Chamlers, which he thought might be a factor that ‘handicapped its ability to make clear choices’ over some defence issues.
Prof Chalmers noted that the document talked about the UK’s ambition to be science and technology superpower but called attention to the fact that research and development spending is below the OSD average, although the ambition was to get to the average. However, this did not meet the stated ambition of international S&T leadership.
Discussing further the stated science and technology ambition, Lord Ricketts stated that although the UK has been good at innovation and science breakthroughs, it has not been as good at translating this into commercial success.
Lord Ricketts also questioned the lack of references to the European Union, “which says very little about our relationship with the EU.”
“It gives the impression of the UK as an agile Power with a range of different partners including other middle Powers…but while the Indo-Pacific tilt isn’t a pivot in military terms, but is more substantial in diplomatic and economic terms.”
In terms of China, Prof Chambers highlighted the toughening stance by the US Biden Administration triggering a robust push-back from China. He suggested that if that gets worse there could be some extent of economic de-coupling.
Talking of whether bilateral relationships with European countries could be maintained post-Brexit, Lord Ricketts opined that the Lancaster House agreement with France over defence-industrial cooperation “has really run out of steam.” But added that the UK should not lose its longer term focus on European security.
US MAJOR ARMS SALES (Defence Security Cooperation Agency – DSCA).
No further updates.
US GOVERNMENT CONTRACTS
Highlighting a selection of $100 million+ government awarded contracts awarded between 29 March – 2 April 2021 and Foreign Military Sales contracts.
2 April
US ARMY
Kokolakis Contracting was awarded a $112 million contract to construct a cyber instructional facility. US Army Corps of Engineers is the contracting activity.
1 April
DEFENSE LOGISTICS AGENCY
Parker Hannifin has been awarded a maximum $1.75 billion contract for aircraft spare parts. Using military services are Army, Navy, Air Force and Marine Corps. The contracting activity is the Defense Logistics Agency Aviation.
US SPECIAL OPERATIONS COMMAND
CACI received a $372 million contract for joint geospatial analytic support services to US Special Operations Command (USSOCOM). The contract will provide proficient and capable geospatial analysts experienced with the processing, exploitation and dissemination of traditional and non-traditional intelligence data. USSOCOM Headquarters is the contracting activity.
US ARMY
Missouri Department of Social Services received a $190 million contract for full food services at Fort Leonard Wood. US Army Field Directorate Office is the contracting activity.
US NAVY
Lockheed Martin, Rotary Mission Systems is awarded a $128 million modification contract to exercise options for full rate production of Surface Electronic Warfare Improvement Program (SEWIP) AN/SLQ-32(V) 6. The Naval Sea Systems Command is the contracting activity.
31 March
US NAVY
Boeing is awarded a $1.6 billion modification contract that provides for the production and delivery of 11 P-8A Lot 12 production aircraft; nine for the Navy and two for the government of Australia. Fiscal 2021 aircraft procurement (Navy) funds in the amount of $1.3 billion; and foreign cooperative agreement funds in the amount of $7.5 million will be obligated at time of award. The Naval Air Systems Command is the contracting activity.
Northrop Grumman Systems is awarded a $195 million modification contract that exercises options to provide support services to include non-recurring engineering, software support activity and product support in support of E-2D Advanced Hawkeye (AHE) Lot 9 full rate production (FRP) aircraft. In addition, this modification adds scope to procure one E-2D AHE CV-22B variation in quantity aircraft Lot 10 FRP aircraft. The Naval Air Systems Command is the contracting activity.
BAE Systems Land & Armaments has received a $76 million modification contract to exercise options to procure MK 41 Vertical Launching System canisters and ancillary hardware. This contract combines purchases for the US government (50 percent); and the governments of the Republic of Korea, Japan, the Netherlands, Norway, Spain, Australia, and Turkey (50 percent combined) under the Foreign Military Sales (FMS) program. Fiscal 2021 weapons procurement (Navy) funds in the amount of $17.3 million (23 percent); FMS Republic of Korea funds in the amount of $12 million (16 percent); fiscal 2021 Defense-Wide Procurement funds in the amount of $11 million (15 percent); fiscal 2020 Defense-Wide Procurement funds in the amount of $9 million (12 percent); FMS Japan funds in the amount of $9 million (12 percent); FMS Netherlands funds in the amount of $7 million (nine percent); FMS Norway funds in the amount of $4.7 million (six percent); FMS Spain funds in the amount of $2.8 million (four percent); FMS Australia funds in the amount of $1.7 million (two percent); and FMS Turkey funds in the amount of $1,1 million (one percent) will be obligated at time of award. The Naval Sea Systems Command is the contracting activity.
MISSILE DEFENSE AGENCY
Lockheed Martin Missiles and Fire Control is being awarded a sole source contract in the amount of $610 million under Foreign Military Sales (FMS) cases to the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA). Under this Phase II contract, the contractor will provide continued efforts initiated in the previously awarded Phase I contract (HQ0147-19-C-0007), as well as efforts related to ground production, training, spares, spares consolidation, software support, facility support, engineering services, obsolescence (pop-up), continental and outside the continental US system integration and check-out, and maintenance. KSA FMS funds in the amount of $610 million will be used to fund this effort. The Missile Defense Agency is the contracting activity.
US AIR FORCE
Northrop Grumman Systems has been awarded a $259 million modification contract for Active Electronically Scanned Array radars of Air Force F-16 aircraft. This modification is for the exercise of options to include 115 production radars, as well as associated spares. Air Force Life Cycle Management Center is the contracting activity.
30 March
US ARMY
Bell Textron was awarded a $292 million modification contract for the Future Long Range Assault Aircraft Competitive Demonstration and Risk Reduction Phase 2. US Army Contracting Command, Redstone Arsenal, Alabama, is the contracting activity.
Sikorsky Aircraft was awarded a $284 million modification contract for the Future Long Range Assault Aircraft Competitive Demonstration and Risk Reduction Phase 2. US Army Contracting Command is the contracting activity.
AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals was awarded a $204 million modification contract for a minimum of 100,000 doses of AZD7442, a combination antibody product intended to prevent or treat clinical effects of SARS-CoV-2. US Army Contracting Command is the contracting activity.
Systems Studies & Simulation was awarded a $9 million modification contract for technical support services for the Precision Fires Rocket and Missile Systems Project Office. Fiscal 2010 and 2021 Foreign Military Sales (Romania and Poland) funds; fiscal 2020 and 2021 research, development, test, and evaluation, Army funds; and fiscal 2019, 2020 and 2021 aircraft procurement, US Army Contracting Command is the contracting activity.
DEFENSE HUMAN RESOURCES ACTIVITY
The Institute of International Education has been awarded a maximum $144 million hybrid contract for administration of the David L. Boren Scholarships, Fellowships, and the Language Flagship institutional awards. Defense Human Resources Activity is the contracting activity.
US NAVY
Raytheon Missiles and Defense has received a $130 million modification contract to exercise options for fiscal 2021 for the Rolling Airframe Missile Block 2/2A Guided Missile Round Pack, spare replacement components and recertification. This contract combines purchases for the US government (66 percent); and the governments of Japan, Turkey and United Arab Emirates (34 percent combined) under the Foreign Military Sales (FMS) program. Fiscal 2021 weapons procurement (Navy) funds in the amount of $84 million (65 percent); FMS Japan funds in the amount of $41 million (32 percent); Fiscal 2021 operation and maintenance (Navy) funds in the amount of $1.8 million (one percent); FMS United Arab Emirates funds in the amount of $1.7 (one percent); and FMS Turkey funds in the amount of $247,023 (one percent), will be obligated at the time of award. The Naval Sea Systems Command is the contracting activity.
Northrop Grumman Systems Marine Systems is awarded an undefinitised contract action (UCA) with a not-to-exceed amount of $69 million under contract modification which will be definitised on or about 1 Sept, 2021. The effort includes production of the launcher subsystem hardware in support of the Columbia and Dreadnought common missile compartment (CMC) program. Fiscal 2019 shipbuilding and conversion (Navy) funding in the amount of $249,999; fiscal 2020 shipbuilding and conversion (Navy) funding in the amount of $8 million; fiscal 2021 shipbuilding and conversion (Navy) funding in the amount of $1.9 million; and fiscal 2021 Foreign Military Sales funding in the amount of $10.5 million will be obligated on this award. Strategic Systems Programs is the contracting activity.
Northrop Grumman Systems is awarded a $30 million modification contract that exercises an option to procure the necessary weapon replaceable assemblies and AN/APR-39D(V)2 support equipment hardware, to include 27 processors, 108 antenna detectors, 82 radar receivers, 27 low band arrays, 16 battery handle assemblies, and 28 circuit card assemblies. Additionally, this order provides non-recurring engineering, technical engineering, management and logistics support services to fabricate, assemble, test, and deliver the AN/APR-39D(V)2 hardware for the Navy, Army, and Foreign Military Sales (FMS) customers. Fiscal 2021 aircraft procurement (Navy) funds in the amount of $27.2 million; fiscal 2021 aircraft procurement (Army) funds in the amount of $1.7 million; and FMS funds in the amount of $998,496 will be obligated at time of award. The Naval Air Systems Command is the contracting activity.
DEFENSE LOGISTICS AGENCY
Olgoonik Federal has been awarded a maximum $125 million IDIQ contract for a wide range of warehouse and distribution operation services. Using customers are Defense Logistics Agency, Defense Department and federal civilian agencies. The contracting activity is the Defense Logistics Agency Distribution.
US AIR FORCE
General Atomics Aeronautical Systems has been awarded a $12 million contract for United Kingdom MQ-9 additional aircraft. Production of one MQ-9 Reaper Block 1, Lynx Synthetic Aperture Radar, Embedded Global Positioning System Inertial Navigation System, and United Kingdom specific modifications will be performed stateside and is expected to be completed July 1, 2021. This award is the result of a sole-source acquisition and involves 100 percent Foreign Military Sales to the government of the United Kingdom. Air Force Life Cycle Management Center is the contracting activity.
29 March
US NAVY
Bechtel Plant Machinery is awarded a $252 million modification contract to exercise an option for naval nuclear propulsion components. The Naval Sea Systems Command is the contracting activity.
Ahtna Logistics; Guard Unit; Hatalom; and Shock Stream, are awarded a combined $124million IDIQ contract for the procurement of services to facilitate design, development, testing, production, and fielding of several simulations/simulated training systems and devices. The Equipment Related Services Contractor Operator and Maintenance Services (COMS)-Systems (S) (COMS-S) multiple award task order contract will be used to issue task orders to provide sustainment support for all existing and any future Marine Corps training systems that are not exclusively utilised on ranges and not subjected to live fire, including, but not limited to: Underwater Egress Trainer; Supporting Arms Virtual Trainer; Combat Vehicle Training Systems; Combat Convoy Simulator; Virtual Combat Convoy Trainer/Reconfigurable Virtual Simulator; Indoor Simulated Marksmanship Trainer; Operator Driver Simulator; Improved Moving Target Simulator; and the Dry Egress Trainers. Marine Corp Systems Command is the contracting activity.
US ARMY
AITC-Five Domains JV was awarded a $37 million contract for readiness, train, advise, assist, and mentor services. Fiscal 2021 Foreign Military Sales (Saudi Arabia) funds in the amount of $37 million were obligated at the time of the award. US Army Contracting Command is the contracting activity.
General Dynamics Land Systems was awarded a $9.5 million modification contract for Abrams Systems technical support. Fiscal 2019 and 2021 other procurement, Army funds; fiscal 2021 research, development, test and evaluation, Army funds; and fiscal 2021 Foreign Military Sales (Saudi Arabia) funds in the amount of $9.5 million were obligated at the time of the award. US Army Contracting Command is the contracting activity.
EVENTS CONFIRMED
AVALON AIRSHOW 2021, Geelong, Australia has been postponed to 30 Nov-5 Dec 2021.
AVALON 2021 was to be held over 23-28 November, but due to a confliction with the rescheduling of the Australian Formula One Grand Prix the airshow has been deferred by one week to new dates of 30 November to 5 December.
CANCELLED EVENT
ROYAL INTERNATIONAL AIR TATTOO 16-18 July, Raf Fairford, UK
Organiser statement: “It is with great regret that the Directors of RAF Charitable Trust Enterprises have taken the difficult decision to cancel this summer’s Royal International Air Tattoo, which was due to take place at RAF Fairford, in Gloucestershire on July 16-18.” RIAT is being planned to return in 2022.
ISDEF, 15-17 June now moved to 9-11 November 2021, at Tel Aviv, Israel
ISDEF 2021 will take place in Tel-Aviv on 9-11 November 9-11 and will bring together companies specialising in the latest equipment and technologies for defense, HLS, mega-event protection, cybersecurity, intelligence, and counter-terrorism, providing a unique platform of advanced technologies and knowledge transfer to ensure public safety.
Photo Quiz answers:
1). No, not a photographer, but the World War II German commander Field Marshal Erwin Rommel, know for his exploits and achievements in France, North Africa and for strengthening the Atlantic Wall before the allied invasion of Europe in June 1944.
2). Major General Orde Wingate, famously recognised for his creation of the Chindit deep-penetration missions in Japanese-held territory during the Burma Campaign of the Second World War.
3). Ending his service at Lieutenant General Lewis Burwell “Chesty” Puller serviced with destinction as a commander with the US Marines in the Pacific during World War II, and later during the Korean War. He was awarded awarded five Navy Crosses and one Army Distinguished Service Cross.

Best wishes,
Andrew Drwiega
Editor-in-Chief
Armada International / Asian Military Review